Sustainability
TCFD
TCFD-Recommended Information Disclosure

The Nitta Group recognizes climate change as a material issue affecting business continuity. In May 2022, we announced our endorsement of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)*. We analyze the risks and opportunities that climate change presents to Group business and endeavor to reflect this in our management strategy and risk management, as well as work to enhance our information disclosure. *The TCFD was established by the Financial Stability Board at the request of the G20 (Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy). It treats climate change as both a risk and opportunity and recommends disclosure of the impact that greenhouse gas-induced temperature rise has on corporate finances.
Governance
For the Nitta Group, addressing environmental challenges, including climate change, is a key management issue. In order to enhance our efforts aimed at meeting the sustainability-related challenges facing society, we established the Sustainability Committee on May 13, 2022 and transferred to it some of the duties which had previously been handled by the CSR Promotion and Risk Management Committee.
The Sustainability Committee is chaired by the president and meets four times a year to deliberate, from a medium-to-long-range and ESG perspective, on the risks and opportunities created by climate change, as well as how the Nitta Group should respond to climate change risks, based on the NITTA Group Mission, the NITTA Group Code of Conduct, and the Sustainable Management Policy. The results of these deliberations are reported four times per year to the Board of Directors, which then deliberates and decides on important matters based on these results.
Sustainability Committee
- Chair
- Representative Director, President, President Executive Officer
- Vice chair
- Representative Director
- Members
- Directors, Audit & Supervisory Board members, general managers of business divisions, etc.
- Secretariat
- Management Administration Department; Safety, Environment, and Quality Group
Corporate Governance System
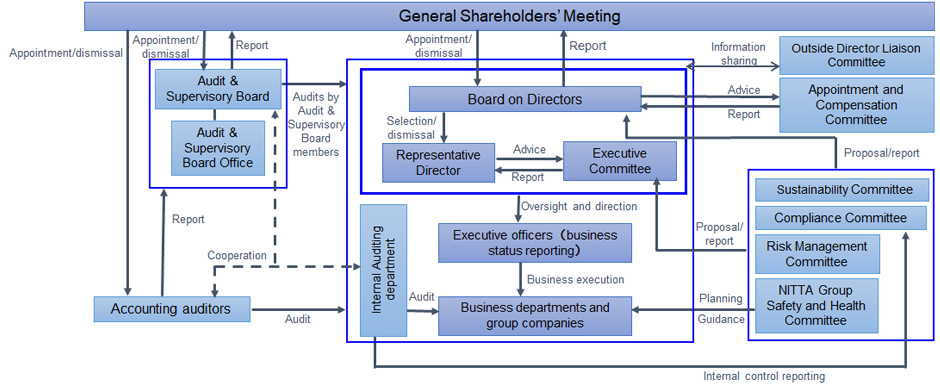
Climate Change-related Governance System
| Organization | Role | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Board of Directors | Decision-making and reporting regarding chief climate change-related matters | 4 times/year |
| Sustainability Committee | Discussion of, and reporting to the Board of Directors regarding, chief climate change-related matters | 4 times/year |
Sustainability Committee Main Agendas
| Held | Main agenda |
|---|---|
| Each quarter |
|
| First quarter |
|
| Second quarter |
|
| Third quarter |
|
| Fourth quarter |
|
Strategies
We have studied the risks and opportunities that climate change presents for Nitta Group business. Among these, we have identified transition risks and opportunities arising from such factors as changing governmental policies, regulations, and other social demands. We have identified physical risks and opportunities arising from such factors as increasingly extreme weather phenomena.
In analyzing possible scenarios, we utilized scientifically grounded scenarios presented by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and others to investigate potential impact on Nitta business. Our most recent scenario analysis looked at the entire supply chain, including raw material and parts procurement, product development, manufacturing, and sales, for the Nitta Group’s belt and rubber products business, hose and tube products business and Air clean products business. We considered the impact that a 4°C temperature rise scenario and 1.5°C temperature rise scenario would have on this business in 2030.
- 4℃ scenario
- This scenario assumes the current level of climate change action is maintained, resulting in an approximately 4℃ rise in average global temperature by the end of this century compared with the average global temperature prior to the industrial revolution. Weather phenomena would become more intense and sea levels would rise, among other effects. On the one hand, physical risks would increase, while on the other hand restrictions on corporate activity and consumer activity would not increase beyond current levels.
- 1.5℃ scenario
- This scenario assumes greater efforts are made to achieve carbon neutrality, resulting in an approximately 1.5℃ rise in average global temperature by the end of this century compared with the average global temperature prior to the industrial revolution. On the one hand, this would limit the increase in physical risks, while on the other hand restrictions on corporate activity and consumer activity, in the form of taxes and laws and regulations, would be stronger.
| Item | Impact on total sales | Impact on business | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4℃ | 1.5℃ | Risk | Opportunity | |||
| Transition | Governmental policies and regulations | Carbon cost (carbon tax) |
─ | 4 |
【1.5℃】 |
─ |
| Emissions trading Response to greenhouse gas emissions regulations |
─ | 2 |
【1.5℃】 |
─ | ||
| Plastic-related regulations | ─ | 3 |
【1.5℃】 |
─ | ||
| Forest conservation-related governmental policies | ─ | 2 | ─ |
【1.5℃】 |
||
| Renewable energy policies | ─ | 2 |
【1.5℃】 |
【1.5℃】 |
||
| Energy-saving policies | ─ | 3 |
【1.5℃】 |
【1.5℃】 |
||
| Technologies | Diffusion of renewable energy and energy-saving technologies | ─ | 3 | ─ |
【1.5℃】 【1.5℃】 【1.5℃】 |
|
| Evolution of low-carbon technologies | ─ | 3 |
【1.5℃】 |
【1.5℃】 【1.5℃】 【1.5℃】 【1.5℃】 |
||
| Market | Evolution of next-generation technologies | ─ | 3 | ─ |
【1.5°C】 【1.5°C】 |
|
| Physical | Acute | Intensifying weather phenomena (typhoons, torrential rains, landslides, storm surges, etc.) |
3 | 1 |
【4℃】 【4℃】 |
─ |
| Chronic | Increasing average temperature | 3 | 2 |
【4℃】 |
【4℃】 【4℃】 【4℃】 |
|
Note: Rating criteria (estimated impact)
| 1 | 10 million yen or less |
|---|---|
| 2 | Over 10 million to 50 million yen |
| 3 | Over 50 million to 100 million yen |
| 4 | Over 100 million yen to 500 million yen |
| 5 | Over 500 million yen |
These analyses, ratings, and the study of countermeasures have been implemented in coordination with an outside consulting firm and based on discussion conducted by the Sustainability Committee.
Moving forward, we will continue to perform regular analyses and rating reviews of risks and opportunities based on trends and changes in the external environment.
Countermeasures
We are pursuing the following initiatives in order to strengthen our resilience in the face of the listed risks.
| Classification | Risk countermeasure policy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| General | Intermediate | Specific | |
| Transition | Governmental policies and regulations | Carbon cost (carbon tax) |
|
| Renewable energy policies |
|
||
| Energy-saving policies |
|
||
| Technologies | Evolution of low-carbon technologies |
|
|
| Physical | Acute | Intensifying weather phenomena (typhoons, torrential rains, landslides, storm surges, etc.) |
|
- Introduce internal carbon pricing
- On April 1, 2023, we introduced and began implementing an internal carbon pricing system at Nitta and its subsidiaries in Japan. Under this system, we use an in-house standard to convert greenhouse gas emissions to monetary values that will inform our capital expenditures.
By setting our internal carbon price at 18,000 yen/t-CO₂ and using this system as one standard for making investment decisions, we will accelerate investments in energy-saving, low- and no-carbon-emitting facilities, thus contributing to reduced CO₂ emissions.
Risk Management
The Nitta Group recognizes that the changes resulting from climate change is a major risk factor and therefore works, through the Sustainability Committee (which was entrusted in May 2022 with the duties previously handled by the CSR Promotion and Risk Management Committee), to assess, avoid, mitigate, and prevent the risks posed by climate change.
As a general rule, the Sustainability Committee meets four times per year and, in order to assess the impact of climate change on Group business, undertakes scenario analyses and other measures to identify, analyze, and rate climate change risks and opportunities. The committee then provides the Board of Directors with a report four times a year on the risks and opportunities it identifies.
Indicators and Goals
The Nitta Group pursues a basic policy of reducing greenhouse gas emissions arising from the production phase and, towards that end, is working to reduce emissions by 46% by fiscal 2030 (compared with fiscal 2013) and to achieve carbon neutrality by fiscal 2050. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we have been advancing three initiatives: (1) thoroughly implement energy-saving measures to reduce energy consumption, (2) expand the use of renewable energy, and (3) purchase greenhouse gas-free energy.
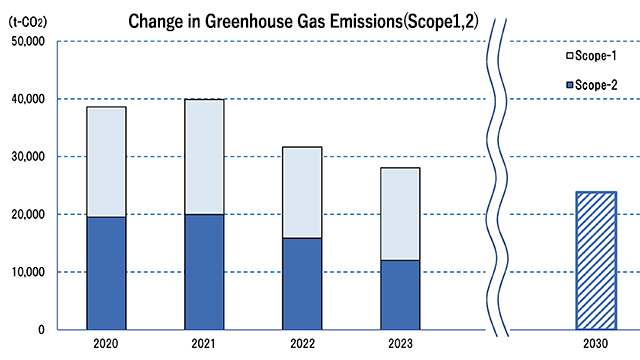
The system covers Nitta Group manufacturing bases, including the Nitta head office, branches and affiliate companies. Emissions at the Nara Plant include those from the production base of an equity-method affiliate on the site.
In this fiscal year, besides energy-efficiency activities based on our environmental management system, we have continued to aggressively introduce renewable energy at all our worldwide bases. At manufacturing bases in China, we have introduced renewable energy using I-REC (International Renewable Energy Certificates), and in fiscal 2023 we achieved a 35% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to fiscal 2013.
We will continue with energy-efficiency efforts as we strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through the introduction of renewable energy at our bases around the world.